A primary-ever dataset bridging molecular details about the poplar tree microbiome to ecosystem-level processes has been launched by a workforce of Division of Vitality scientists led by Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory. The mission goals to tell analysis concerning how pure methods perform, their vulnerability to a altering local weather, and finally how crops may be engineered for higher efficiency as sources of bioenergy and pure carbon storage.
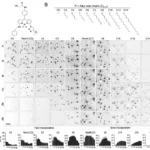
The info, described in Nature Publishing Group’s Scientific Knowledge, gives in-depth info on 27 genetically distinct variants, or genotypes, of Populus trichocarpa, a poplar tree of curiosity as a bioenergy crop. The genotypes are amongst people who the ORNL-led Heart for Bioenergy Innovation beforehand included in a genome-wide affiliation examine linking genetic variations to the timber’ bodily traits. ORNL researchers collected leaf, soil and root samples from poplar fields in two areas of Oregon — one in a wetter space topic to flooding and the opposite drier and prone to drought.
Particulars within the newly built-in dataset vary from the timber’ genetic make-up and gene expression to the chemistry of the soil atmosphere, evaluation of the microbes that dwell on and across the timber and compounds the crops and microbes produce.
The dataset “is unprecedented in its measurement and scope,” stated ORNL Company Fellow Mitchel Doktycz, part head for Bioimaging and Analytics and mission co-lead. “It’s of worth in answering many alternative scientific questions.” By mining the information with machine studying and statistical approaches, scientists can higher perceive how the genetic make-up, bodily traits and chemical range of Populus relate to processes akin to biking of soil nitrogen and carbon, he stated.
“The information we generated from this one plant might be folded again into tasks that produce biofuels from poplar,” stated Melanie Mayes, chief of ORNL’s Ecosystem Processes group and a collaborator on the mission. “The process we constructed right here might be wanted for bioengineering of different crops, and to assist us construct local weather resilience — to advance soil carbon storage and cut back greenhouse gasoline emissions.”
The whole dataset includes greater than 25 terabytes. Hyperlinks to the information can be found as a part of the Nationwide Microbiome Knowledge Collaborative, or NMDC, a DOE initiative supporting data-sharing on the affiliation of microbiomes with environmental processes.
“The dataset represents the most important publicly accessible metagenomics repository on a tree endosphere,” the plant tissue atmosphere that’s residence to advanced microbial communities, stated Christopher Schadt, mission co-lead and ORNL distinguished workers scientist.
Detailed analyses of the samples resulted in 318 metagenomes, revealing the variety of microbes residing in and round timber by way of genetic sequencing. Ninety-eight plant transcriptomes present info on the total vary of messenger RNA molecules expressed within the plant roots. The dataset contains 314 metabolomic profiles, supplying info on the small molecules produced by crops and microbes as they develop or in response to emphasize. Knowledge are additionally included on related soil bodily and biogeochemical traits, analyzing chemical substances current and the way they cycle by way of the atmosphere.
Integrating this “multi-omics” knowledge will present important info to scientists learning how plant-related molecular and mobile occasions are linked to ecosystem processes and behaviors.
Understanding plant, soil nitrogen biking triggers
The Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Workplace of Science person facility at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory, was an in depth collaborator on the mission. JGI led the metabolomics profiling of the leaf, root and soil atmosphere, or rhizosphere, the plant root transcriptomics sequencing, and the soil rhizosphere and endosphere metagenomics work.
“The mix of metagenomics and metabolomics from leaf, root and soils, together with Populus host transcriptomes, make this a very distinctive dataset for the analysis neighborhood and will function a central knowledge useful resource to discover plant-microbe interactions,” stated Emiley Eloe-Fadrosh, Metagenome Program head at JGI.
The mission started as an ORNL pilot referred to as Bio-Scales, supported by the Organic Programs Science Division within the DOE Workplace of Science’s Organic and Environmental Analysis program. Bio-Scales pursues a greater understanding of the plant-microbe relationship with a concentrate on nitrogen biking. Nitrogen is a vital nutrient for all times, however when overused in agriculture and different purposes it will probably hurt water high quality or be emitted because the potent greenhouse gasoline nitrous oxide, or N2O.
“The mission required the mixing of numerous various experience,” Doktycz stated. “It began with a workforce who went out within the midst of COVID-19 to gather all these various supplies and received them again to the lab, then ready, analyzed and extracted knowledge from them. We additionally had an unimaginable technical assist workforce who processed a whole bunch of those samples in a tracked and coordinated manner, interfacing with the Joint Genome Institute for the sequence evaluation.”
Along with its measurement and scope, the dataset stands out as being closely annotated with metadata — with exact particulars, as an example, on the place and the way the sampling came about and an ordinary format for subsequent knowledge reporting. Including these parts to knowledge makes info simpler to search out, perceive and reuse.
ORNL’s Stanton Martin, who led knowledge administration for the mission in shut coordination with the NMDC, famous that the data-first strategy helps synthetic intelligence and different analytical approaches to assist resolve scientific questions. “The info administration we carried out on this mission is massively invaluable to knowledge practices for different tasks just like the Plant-Microbe Interfaces Scientific Focus Space and the Heart for Bioenergy Innovation at ORNL. It performs to ORNL’s strengths in what I name knowledge administration’s three V’s — knowledge quantity, selection and velocity — and allowed us to take a primary step in integrating very giant ‘omics knowledge in a manner that has not been carried out earlier than.”
The mission began with Schadt and Mayes touring to Oregon for sampling. “It usually would have been six scientists, however we had journey restrictions on teams touring collectively as a result of pandemic,” Schadt stated. In addition they needed to work round encroaching wildfires, as Oregon skilled an lively fireplace season that 12 months. Schadt and Mayes labored with the help of Oregon State College volunteers to assemble in depth geotagged samples on the two websites.
Helpful bioengineering
Mayes stated the mission “will get on the position of genes in influencing not simply the destiny of the plant itself, but additionally the atmosphere round it, such because the soil. For example, we needed to know the potential of soil microbes to both make extra nitrate or to take away extra nitrate from the system. We needed to be taught extra about how plant genomics affect what soil microbes are doing.” Understanding extra concerning the plant and soil nitrogen cycle can have an effect on emissions of N2O, a gasoline that accounts for six% of all greenhouse gasoline emissions in the US.
“If you already know which genes to focus on that consequence within the minimization of N2O or nitrate manufacturing, then you will have the potential to have an effect on each greenhouse gas-related warming and water high quality,” Mayes stated. “You possibly can, as an example, choose and additional bioengineer crops with the very best genetic profile for controlling these emissions.”
“This mission is exclusive as a result of it will get on the connection between plant genomes and environmental outcomes like nitrous oxide emissions or nitrate manufacturing,” Mayes stated. “Constructing one of many first, complete datasets on the plant-microbe relationship additionally tells us how a lot we nonetheless can be taught.”








No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel